Capability Map
Why a Capability Map for CIVITAS/CORE?
The CIVITAS/CORE Capability Map is designed to represent the platform’s capabilities at an abstract level, independent of the implementing technical systems. It provides a means to define the platform’s capabilities without preemptively specifying a technical architecture. The logical structure of the platform is used visually to create an initial separation of capabilities from one another.
We use the Capability Map to identify redundancies and gaps, as well as to guide solution selection based on capabilities. Decisions derived from this process are documented in ADRs (Architecture Decision Records).
CIVITAS/CORE Capability Map
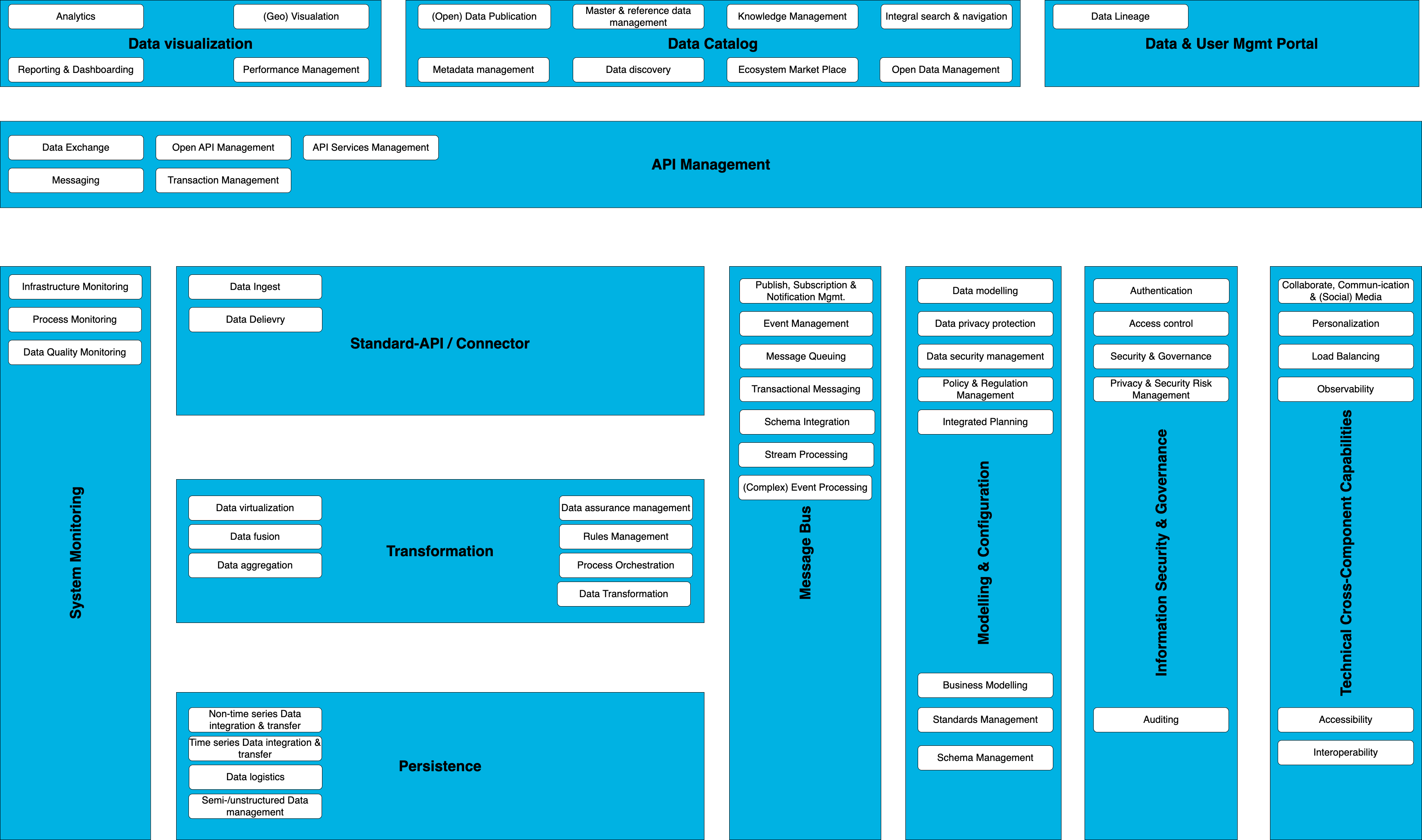
The CIVITAS/CORE Capability Map always represents a snapshot in time. It can and will continue to evolve as work progresses.
Capability Definitions
Data Visualization
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Analytics | Enables the analysis of data for descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive purposes. It identifies patterns and trends, turning raw data into actionable insights. | |
| Reporting & Dashboarding | Focuses on presenting analytics results in clear reports and dashboards. It helps track insights and communicate data effectively. | |
| (Geo) Visualization | Delivers data and insights in graphical, geographical, or interactive formats to enhance understanding. It supports dynamic exploration through features like zooming, filtering, and layering. | |
| (Open) Data Publication | Facilitates sharing data with defined or public audiences in standardized formats and through multiple channels. It ensures reliable and timely access to information for reuse and analysis. |
Data Catalog
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Master & Reference Data Management | Ensures consistent management of core, non-transactional data about entities, objects, and their attributes. | |
| Knowledge Management | Focuses on capturing, sharing, and applying knowledge to drive innovation and improve collaboration. | |
| Integral Search & Navigation | Provides tools to search and browse structured and unstructured data across multiple sources. It improves data accessibility and findability through navigation and keyword search. | |
| Metadata Management | Governs and documents data definitions, ownership, lineage, quality, and classification. It creates transparency and supports trust in data by managing “data about data.” | |
| Data Discovery | Supports exploration and understanding of datasets to uncover patterns, relationships, and insights. It uses visual exploration. | |
| Ecosystem Market Place | Offers a platform for publishing and consuming datasets, applications, and services with processes for (licensing and) authorization. It promotes standards, transparency and innovation within data ecosystems. | |
| Open Data Management | Enables the publication, use, and governance of open data while ensuring privacy and security. It fosters collaboration, innovation, and transparency through standardized formats and community engagement. |
Data & User Mgmt Portal
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Lineage | Tracks data across its entire lifecycle, from source through transformations to final use. It ensures transparency and traceability, helping maintain trust, support compliance, and optimize data flows. |
API Management
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Exchange | Enables the transfer of data between systems and organizations using standardized formats and protocols. | |
| Open API Management | Oversees the design, publication, and governance of APIs, including policies, access control, and usage tracking. It ensures secure and efficient access to system functionality and data for internal or external users. | |
| API Services Management | Manages the lifecycle of services such as APIs, data exchanges, and publications through catalogs, versioning, contracts, and monitoring. It ensures reliable and scalable service delivery. | |
| Messaging | Facilitates automated communication between systems through message exchange, including queuing, brokering, and publish/subscribe models. It supports decoupled and efficient system interactions. | |
| Transaction Management | Ensures the consistent recording and synchronization of transactions across systems and organizations. It supports legal, contractual, and operational requirements for accuracy and integrity. |
System Monitoring
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Monitoring | Continuously tracks and analyzes the performance, availability, and health of IT systems and components. It collects and processes metrics, logs, and events to detect issues early, optimize resources, and ensure system reliability. | |
| Process Monitoring | Automates the observation of business processes based on defined workflows and rules. It supports early detection of process deviations and improves operational efficiency. | |
| Data Quality Monitoring | Continuously measures and validates data accuracy, completeness, and consistency using automated checks and alerts. It helps maintain trust in analytics, ensures compliance, and keeps data fit for purpose across systems. | |
| Performance Management | Focuses on tracking and demonstrating performance gains using defined metrics and benchmarks. It supports comparability, transparency, and progress measurement, often aligned with sustainability and climate goals. |
Standard-API / Connector
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ingest | Collects and transfers data from multiple sources into central systems for processing and analysis. It supports diverse formats and integration methods. | |
| Data Delivery | Distributes data securely and reliably to systems, applications, or users in the required format and timing. |
Message Bus
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Publish, Subscription & Notification Mgmt. | Manages subscriptions and notifications for events or publications from various actors. | |
| Event Management | Oversees events detected by event processing or other sources, triggering processes, alerts, or actions. | |
| Message Queuing | Enables asynchronous communication between distributed systems and services by decoupling producers and consumers. | |
| Transactional Messaging | Guarantees reliable, ordered delivery of messages within business transactions using mechanisms like commit and rollback. | |
| Schema Integration | Aligns and harmonizes data from multiple sources by resolving naming, structure, and type differences. | |
| Schema Integration | Event-driven distribution of models (via Message Bus) | Works with common message Bus via connectors. Example: Update Schema -> shared via Message Bus |
| Schema Integration | Schema Distribution & Caching | Make models easy to cache at gateways/edges and keep them fresh. Example: validators fetch once, then auto‑refresh on change. |
| Stream Processing | Processes and analyzes data streams in real time to enable instant insights and actions. | |
| (Complex) Event Processing | Detects and analyzes patterns across event streams to trigger automated, real-time responses. |
Transformation
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Assurance Management | Monitors, validates, and improves data quality across dimensions like completeness, accuracy, and compliance. | |
| Rules Management | Defines and manages business rules for automated processing, including data validation, process flow, and authorization policies. | |
| Process Orchestration | Automates business process execution based on defined workflows and rules. It coordinates tasks across systems and people. | |
| Data Transformation | Converts, enriches, and structures data to meet required formats and standards for integration and analysis. | |
| Data Virtualization | Provides access to data stored in different systems without requiring physical replication. | |
| Data Fusion | Combines data from multiple sources to create a unified view of entities or events. | |
| Data Aggregation | Summarizes data by grouping entities and calculating aggregates such as totals, averages, or extremes. |
Modelling & Configuration
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Modelling | Structures data by defining entities, attributes, and relationships, often represented in diagrams like entity-relationship or object-oriented models. | |
| Data Privacy Protection | Safeguards personal and sensitive data through policies, controls, and techniques like masking, encryption, and anonymization. | |
| Data Security Management | Protects data confidentiality, integrity, and availability through authentication, authorization, zoning, and intrusion detection. | |
| Policy & Regulation Management | Manages policies and regulations to enable innovation, reduce administrative burden, and improve consistency. | |
| Integrated Planning | Coordinates planning across sectors and administrative boundaries to optimize costs, resources, and impact. | |
| Business Modelling | Analyzes and designs organizational structures, processes, and value creation logic to guide strategy and operations. | |
| Standards Management | Promotes consistency and interoperability through the adoption and coordination of standards across sectors and organizations. | |
| Standards Management | Semantic Interoperability | Common data model supports linked data (JSON-LD, RDF). Example: “bikes_available” vs “availableBikes” map to the same property. |
| Schema Management | Defines, maintains, and governs data models to ensure consistency, version control, and scalability. | |
| Schema Management | Schema Versioning | Enable safe schema evolution without breaking existing clients. Example: Upgrade traffic sensor schema v1→v2 without affecting devices using v1. |
| Schema Management | RBAC & Governance | Control who can modify schemas for compliance and safety. Example: Team A cannot modify Team B’s schemas. |
| Schema Management | Audit Trail | Keep complete versioned history of changes for accountability. Example: Track which user changed a schema that caused an error. |
| Schema Management | Multi-Format Support | Store schemas in multiple formats (Avro, JSON Schema, Protobuf, NGSI-LD/JSON-LD, XSD, RDF, ECORE). No Transformation (Input = Output). Example: Register traffic schemas in all formats used in the city. |
| Schema Management | Format Transformation | Convert schemas between formats. Example: Input JSON and output ECORE or XSD. |
| Schema Management | Compatibility Rules | Ensure schema evolution without breaking old clients. Example: backward/forward compatibility for traffic sensors. |
| Schema Management | Transformation Model Specifications | Store versioned mappings/transformations between models. Example: Map source schema “Baum” to target schema “CCBaum” using e.g. JSONata. |
| Schema Management | High-Throughput Validation | Validate schemas quickly under high load. Example: Busy IoT events do not slow down schema validation. |
| Schema Management | Rollback & Version Pinning | Revert to a prior version safely; clients can pin to a stable schema. Example: Roll back v2 to v1 if issues occur. |
| Schema Management | Lifecycle Management | Manage schema states (e.g. draft → active → deprecated → retired). Example: Domain owner deprecates an outdated schema. |
| Schema Management | Schema Type-Safety & Validation Robustness | Ensures correctness and consistency of schemas via type checks and robust validation to catch issues early. Example: Validate that schemas conform to defined types and formats before storage |
| Schema Management | Open Standards | Supports e.g. NGSI-LD (Smart Data Models), SensorThings models, API compatibility, . Example: import/export municipal data standards. |
Information Security & Governance
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Verifies the identity of users, devices, or systems using credentials like passwords, tokens, or biometrics. | |
| Access Control | Manages access rights through authorization, authentication, approval, and auditing. | |
| Security & Governance | Establishes frameworks and processes to align security strategies with business goals and regulations. | |
| Privacy & Security Risk Management | Identifies, assesses, and prioritizes privacy and security risks, applying resources to mitigate threats and minimize impact. | |
| Auditing | Monitors and records user and administrative actions, including access, updates, and configuration changes. |
Technical Cross-Component Capabilities
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Collaborate, Communication & (Social) Media | Provides digital platforms and services for collaboration between public and private actors, including citizen engagement. | |
| Personalization | Delivers tailored services, data, and interfaces to individuals or groups while ensuring compliance with privacy and security regulations. | |
| Load Balancing | Distributes workloads evenly across available system resources to ensure high availability and performance. | |
| Observability | Collects and analyzes telemetry data such as logs, metrics, and traces to provide insight into system health. | |
| Accessibility | Designs and delivers inclusive products, services, and environments accessible to all users, regardless of ability. | |
| Interoperability | Works with standard data sources via connectors/adapters. Example: integrate with brokers or gateways without custom modifications. |
Persistence
| Capability Name | Sub-Capability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Non-time Series Data Integration & Transfer | Integrates, transforms, and harmonizes data from non-time-series sources such as administrative, document, or media data. | |
| Time Series Data Integration & Transfer | Combines and synchronizes streaming or time-series data from sensors, devices, or events in near real time. | |
| Data Logistics | Manages data storage, retrieval, backup, and archiving across distributed systems and networks. | |
| Semi-/Unstructured Data Management | Handles and analyzes semi-structured or unstructured data such as text, images, or videos. |