Data spaces in FROST
To configure the data space model of the platform in the FROST-Server, we group the key entities of the FROST-Server SensorThings model, e.g. things, into projects. To define the user's access to the entities within each project, users are assigned to project-specific roles. This ensures that data access and manipulation are tightly controlled through role-based permissions, allowing users to interact only with the entities relevant to data spaces (i.e., projects) they have access to.
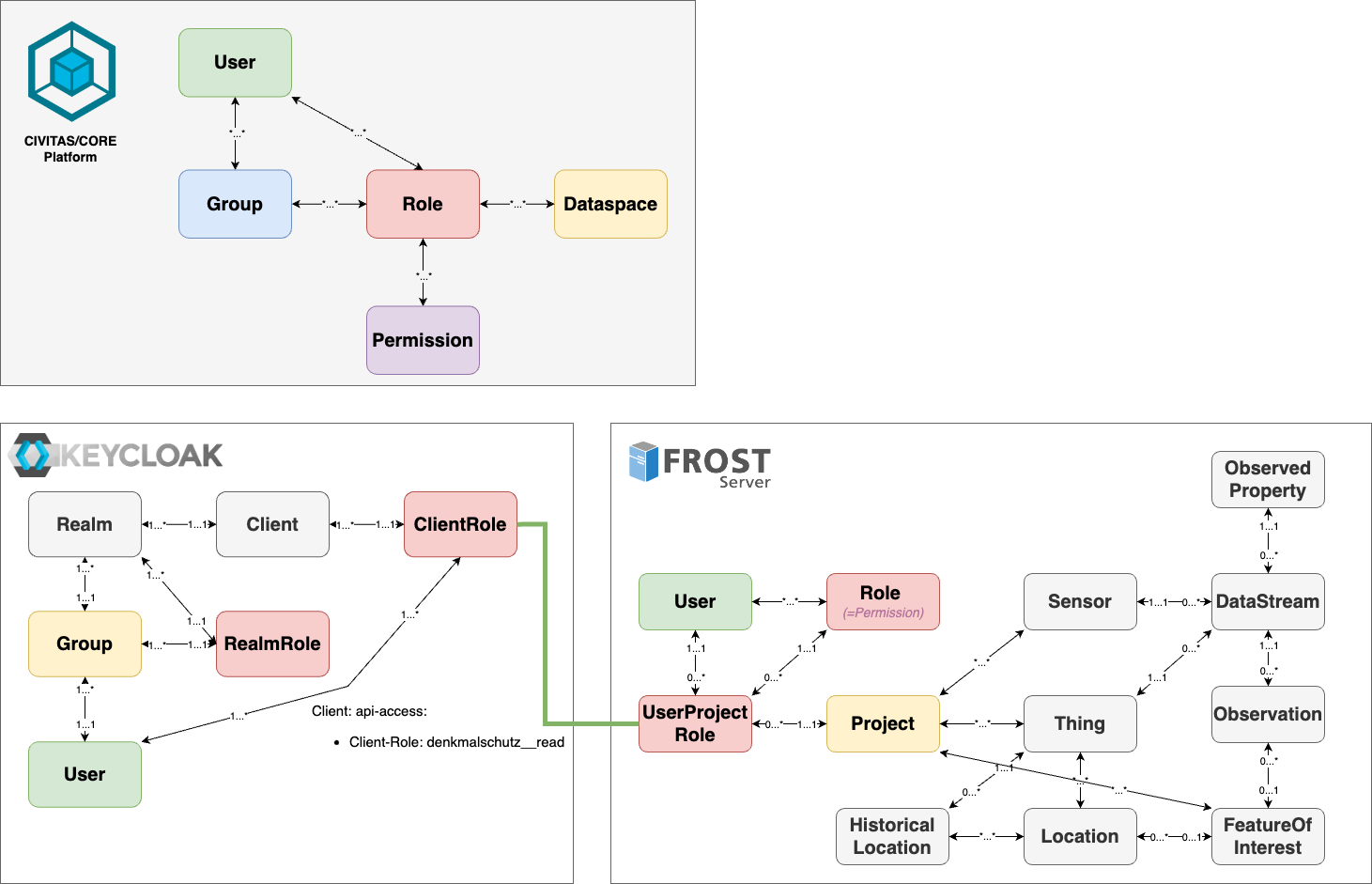
How the Platform's Data space Concept Maps to the FROST-Server
For each Project in the FROST-Server, users are assigned UserProjectRoles that define their access to sensors, data streams, and observations in the corresponding project (i.e., data space).
- User: A person or system entity that accesses FROST-Server to manage FROST-Server entities. Users are assigned global and data space-specific roles that define what actions they can perform within a data space.
- Project: A project represents a data space and serves as a grouping mechanism for all FROST-Server entities. Users must be assigned specific roles within a project to access and manipulate linked entities (see UserProjectRole).
- Roles: Roles define a user's global permissions (CRUD) independently from projects/data spaces. For example, the read role grants global read permissions, allowing the user to read all FROST-Server entities (e.g. Thing, Observation) in all projects.
- UserProjectRole: UserProjectRole allows assigning a user a specific role within a specific project (data space), governing their ability to read, write, or manage sensor data streams and related entities in the project.
- FROST-Server Entities: Core data objects in the FROST-Server consist of Things, Sensors, DataStreams, Observations, FeaturesOfInterest, Locations, HistoricalLocations, and ObservedProperties. These elements form the FROST-Server SensorThings model, which is part of the FROST-Server.
Example for Keycloak and the FROST-Server
The following settings describe the data spaces named "baumkataster" and "denkmalschutz" defined in Keycloak and the FROST-Server:
- Keycloak client "api-access":
- Roles for data space "baumkataster":
baumkataster__read,baumkataster__create,baumkataster__update,baumkataster__delete - Roles for data space "denkmalschutz":
denkmalschutz__read,denkmalschutz__create,denkmalschutz__update,denkmalschutz__delete
- Roles for data space "baumkataster":
- Keycloak client scopes "api:read", "api:write" and "api:delete":
- In the scope "api:read", all read roles (
baumkataster__read,denkmalschutz__read) are added under theScopesection - In the scope "api:write", all write roles (
baumkataster__create,baumkataster__update,denkmalschutz__create,denkmalschutz__update) are added under theScopesection - In the scope "api:delete", all delete roles (
baumkataster__delete,denkmalschutz__delete) are added under theScopesection
- In the scope "api:read", all read roles (
- Keycloak user "Max Mustermann" (
max@mustermann.de)- User-Role-Assignments:
baumkataster__read,denkmalschutz__read,denkmalschutz__create
- User-Role-Assignments:
- FROST-Server projects:
baumkataster,denkmalschutz - FROST-Server global roles:
read,create,update,delete,admin(default roles, always existing)
If Max requests a resource from the FROST-Server and therefore logs into the FROST-Server (via the Keycloak),
- Keycloak sends an access_token: (user:
max@mustermann.de, roles: [baumkataster__read,denkmalschutz__read,denkmalschutz__create]) - The FROST-Server creates a User:
max@mustermann.de(if not already existing) - The FROST-Server creates three UserProjectRoles: (
max@mustermann.de,baumkataster,read), (max@mustermann.de,denkmalschutz,read), (max@mustermann.de,denkmalschutz,create) - The FROST-Server checks the concrete HTTP request with the created UserProjectRoles.
Mapping illustrated
The mapping between platform components and the FROST-Server's data model is illustrated in the diagram below, using colors to represent corresponding objects.
Setting Up Data spaces in the FROST-Server
Based on the roles assigned in Keycloak, global and project-specific roles are created in the FROST-Server. These roles define the user's permissions within the data space, enabling them to interact with the FROST-Server Entities associated with the project (data space).
For more information about how to administer the FROST-Server, please refer to the Admin Guide.