Open Source Standards
The selection of open source components for integration into CIVITAS/CORE follows a defined process. This basically consists of three steps:
- Application of MUST-criteria
- Risk assessment
- Selection decision
BSI TR-03187 Criteria
BSI TR-03187 defines a number of criteria pertinent to the selection of components. There are both mandatory (MUSS) and non-mandatory (SOLL) criteria. Mandatory criteria must be fulfilled by the component. For SOLL criteria, a risk assessment needs to be made and potentially compensating controls need to be implemented.
Depending on the granularity of the component, architectural requirements might additionally apply, e.g. for a database or an authorization component.
| Number | Requirement | Level | SOLL/MUSS |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR-2 | Clientseitige Technologien mit bekannten Sicherheitsschwächen (bspw. NSAPI, Flash, ActiveX oder Java-Applets) DÜRFEN NICHT verwendet werden. Die Sicherheitseigenschaften clientseitiger Technologien SOLLEN dem Stand der Technik entsprechen. | 1 | SOLL |
| AR-11 | Alle verwendeten kryptographischen Verfahren SOLLEN gemäß TR-02102-1 ausgewählt und verwendet werden. | 1 | MUSS |
| AR-22 | Softwarekomponenten von Drittanbietern MÜSSEN von offiziellen, authentifizierten Paketquellen bezogen werden. Die Integrität der Komponenten SOLL erfolgreich signaturbasiert validiert werden. | 2 | SOLL |
Risk Assessment
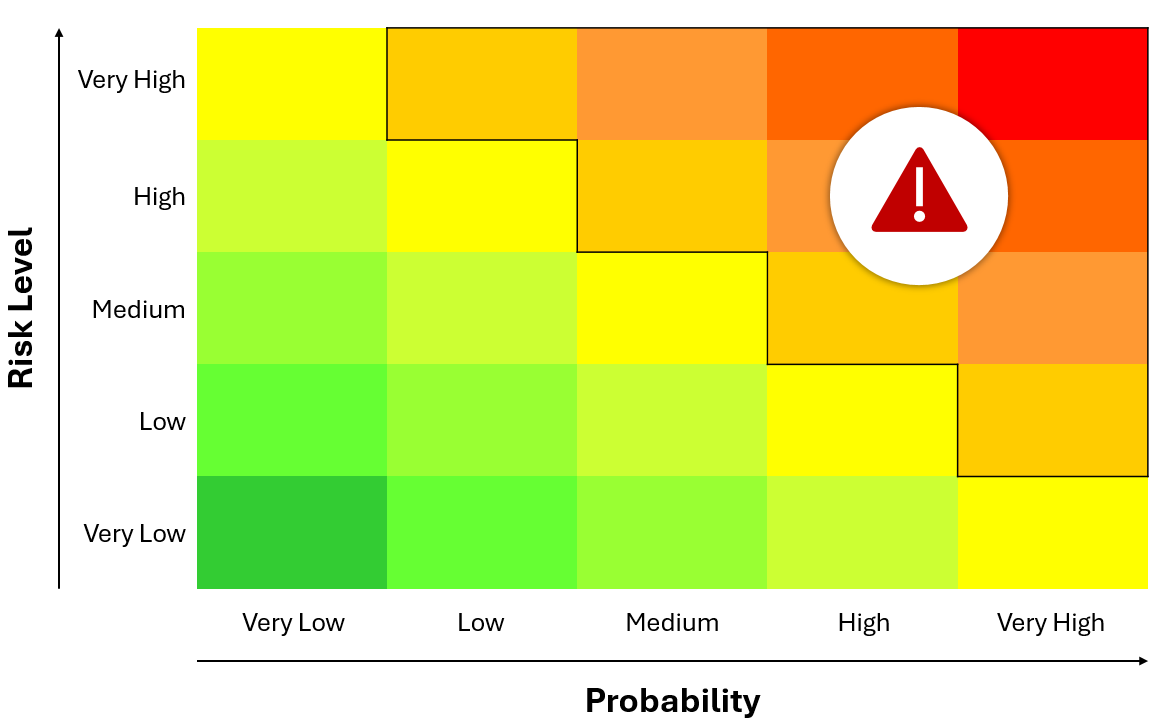
To assess the risk of using the software, criteria were defined for various categories. These criteria were then rated on a 5-point scale (Very Low, Low, Medium, High, Very High), which describes the potential risk if the criterion is not met. In addition, limit values are defined for each criterion, which also describe on a 5-point scale how likely the risk is to occur at a given value.
For some criteria, there are tools available to determine the probability. These are listed in the last column of the table.
| Criterion | Risk Level | Probability Scale | Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community | |||
| Stars | Medium | Very Low: ≥ 10.000 Low: 2.000 – 9.999 Medium: 500 – 1.999 High: 100 – 499 Very High: < 100 | |
| Contributors | Medium | Very Low: ≥ 50 Low: 20 – 49 Medium: 5 – 19 High: 2 – 4 Very High: 1 | |
| Contributors from Various Organisations | Medium | Very Low: > 5 Low: 4 - 5 Medium: 2 - 3 High: 1 Very High: - | |
| Governance Transparency & Decision-Making | High | Very Low: - Roles/docs clear - open RFCs - all decisions/roadmaps written & public Low: - Documentation exists - roles mostly clear - decisions often public Medium: - Partial/dated docs - one org leads - some decisions public High: - No docs - one org controls - mostly private Very High: - Intransparent - no docs - no visible process | |
| Licence | |||
| Licence | Very High | Very Low: open code supported licence Low: OSI-approved license Medium: - High: - Very High: no licence | Check the probability of low Check the probability of very low |
| Maintained | |||
| Project age | Medium | Very Low: > 5 years Low: 3–5 years Medium: 1–3 years High: 6–12 months Very High: < 6 months | |
| Last Commit by a human | High | Very Low: < 1 week Low: 1 week – 1 month Medium: 1 – 6 months High: 6–12 months Very High: > 12 months | |
| Median time needed to close an issue | Medium | Very Low: < 3 days Low: 3 - 6 days Medium: 1 – 2 weeks High: 2 - 4 weeks Very High: > 4 weeks | https://isitmaintained.com/ |
| Percentage of open issues | Low | Very Low: < 10% Low: 11% - 20% Medium: 21 – 35% High: 36% - 50% Very High: > 50% | https://isitmaintained.com/ |
| Repository | |||
| Code-Review | Very High | Very Low: Multiple reviewer Low: All merge requests Medium: - High: Only external merge requests Very High: No Code-Review | |
| Continuous Integration | High | Very Low: - Build - Linting - Unit-Tests - Integration-Tests - Security-Scans Low: - Build - Linting - Unit-Tests Medium: - Build - Linting High: - Very High: No CI/CD | |
| Documentation | |||
| User Manual | Very High | Very Low: Features fully documented with examples Low: Features fully documented Medium: Multi-page documentation High: Small Section in README.mdVery High: No User Manual | |
| Developer Documentation | High | Very Low: Fully documented Sourcecode with Contributor Guidelines Low: Fully documented Sourcecode Medium: Partly documented Sourcecode High: Small Section in README.mdVery High: No Developer Documentation |
Selection decision
Once the risk assessment has been successfully completed, a risk matrix can be created for each piece of software to be evaluated based on the results. Once this has been done for each piece of software, each risk matrix is aggregated so that each piece of software is represented by a point on the risk matrix. This matrix then helps to select the software with the lowest risk. If software is to be selected despite risky criteria, the reasons for the decisions regarding these criteria must be documented in detail.